| |
Barcode Scanner
- How to select the right barcode scanner
- Types of scanner engines - What is the difference
- Barcode Density
- Interface types
1. How to select the right barcode printer
- What type of environment will the scanner be used in ?
- This is to decide on the durability of the scanner.
- Generally, the more often the scanner is used, the more durable the scanner should be.
- Sample of scanner types for different environments.
| Retail |
: Laser with stand / Hands-free Omnidirectional Scanner |
| Hypermarket |
: Linear for heavy usage. Increases scanning throughput. |
| Warehouse / Manufacturing |
: Linear / Area Imager for rugged use. |
| Healthcare |
: Laser / Healthcare scanner. |
| In the office |
: CCD for basic use. |
- What is the size of the items being scanned ?
- If it is too big (such as furniture), you may not be able to bring the item to be scanned.
Suggest to use a cordless/wireless scanner that uses Bluetooth.
Scan data will be sent directly to the PC via a cradle / receiver.
- Is hand-free or a hand-held capability required ?
- Some scanners come with a stand.
- This gives more flexibility for the person using it as both hands are free, thus the term – hands-free.
- Mostly used in high frequency businesses like hypermarket.
- Hand-held scanners are usually cheaper as it cuts the cost of stand.
- What will the scanner connect to ?
- Scanner mainly have 3 interfaces that connects to the PC.
- Be sure to inform before purchasing.
- Ensure the PC also has the interface to connect with scanner.
- USB (most common)
- RS232 / Serial
- Keyboardwedge / PS2
- Do I need to support 1D or 2D or both symbols ?
| 1D Barcode |
2D Barcode |
| Made of vertical black lines |
Mostly square in shape |
| Limited information depending on barcode width & label |
Can cater to more information with less space needed |
| Less cost |
Higher cost |
| Can only scan 1D barcodes |
Can scan both 1D & 2D barcodes |
| Good if label size if no issue |
Good if label needs to be small |
| Good if there are plans to only use 1D |
Good if there are plans to expand to 2D |
- What is the barcode size ?
- All barcodes have a standard size.
- Barcode size relates back to the label size that can fit the barcode.
- Decide first the maximum label size that is acceptable in terms of height & width.
- When generating the barcode and if it can fit in the label, then you can proceed.
- If you have a 1D barcode and after shrinking it to the smallest size, and yet it cannot fit in a label, you may consider 2D barcodes.
- Get a consultant or barcode scanner provider to advise.
- Do I need an environmentally sealed (IP rated) scanner?
- IP stands for Ingress Protection.
- It is rated based on Dust & Water resistance.
- Some scanners comes with this certification.
- How far is the scanning going to be from the PC ?
2. Types of scanner engines - What is the difference
- Laser
- Emits a thin red line.
- Sensitive and easily scans the barcode.
- Able to scan a barcode from a distance of around 17 inches.
Advantage :
- Provides more productivity and accuracy.
Disadvantage :
- Less durable compared to other scanner types like CCD and Linear.
- May not be sensitive on coloured based label. More suitable on white based labels.
- CCD
- Emits a broad red line.
- Required to be near contact (almost touching) with the barcode in order to read.
Advantage :
- Low cost & quite durable.
Disadvantage :
- Not suitable for medium to heavy scanning as the throughput is low.
- Linear Imager
- Emits a broad line similar like CCD scanner except the light source is much brighter and this means it is easier to scan.
- Able to scan from further distance like laser scanner.
Advantages :
- More durable than laser scanner.
- Able to scan damaged or least visible barcodes.
- Easy to scan on coloured based labels.
- Able to scans from a distance like laser scanner.
Disadvantages :
- Cost is normally higher than laser & CCD scanner.
- Area Imager (2D)
- Emits a lights similar like a touch light.
- Specifically made to scan 2D barcodes like QR Code and Data Matrix.
- Can store a lot more characters (up to 50 and more) in a small space.
Advantages :
- Saves time. Instead of scanning multiple barcode information many times, you can combine all the information in one 2D barcode.
- Can scan all types of barcode. 1D and 2D barcodes. (1D scanners cannot scan 2D barcodes)
- More business opportunity such as couponing and redemption. Some 2D scanner is able to scan 2D barcodes via mobile screen.
- Easy to scan the barcode.
- High possibility to scan damaged barcodes.
- Scans faster than laser as there is no need to aim & align with the barcode. It can also scan in any orientation.
- Offers speed & efficiency.
- Able to take photo (monocrome).
- Contains more information in less space.
- Reliable as it on has one moving part. Less parts means less chances to be spoilt.
Disadvantages :
- Not suitable to scan multiple 1D barcodes which is near to each other.
- Higher priced.
- Omnidirectional
- Emits the same red light just like laser scanners. Unlike one single light generated by the laser scanner, it generates 20 lines in a shape like a spider web.
- Can help expedite the scanning process.
- Suitable for high volume scanning for like Hypermarkets.
- Simply bring the barcode across the omnidirectional scanner instead of bringing the scanner to the product saving previous time.
- This will also offer freedom as it is hands free.
Advantages :
- Offers very high productivity.
- Allows more freedom without the need to hold on to scanner.
Disadvantages :
- Higher investment compared to single line scanners.
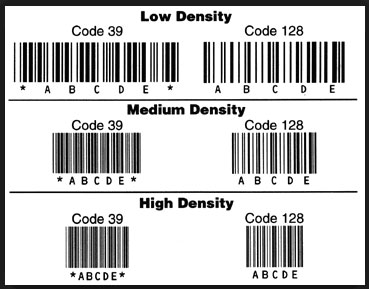
3. Barcode Density
- Most barcodes are ‘Low Density’ or ‘Medium Density’. The higher the density, the more narrow the barcode is. ‘High density’ barcode may be used due to the limited space available to label the barcode info.
- It is important to ensure that if you are going to use a ‘High Density’ barcode, make sure that the barcode scanner/reader is able to capture the ‘High Density’ barcode.
- Note diagram below, there are 2 types of barcode symbologies, Code 39 & Code 128.
All 3 density have same information ‘ABCDE’ but the width is different.
4. Interface types
- The interface is together with the cable. It is to connect the scanner with the PC.
- Most common interface is USB.
- Other interface are; RS232 (Serial) & PS2 (Keyboardwedge).
|
|